Xanthine Oxidase - Manual
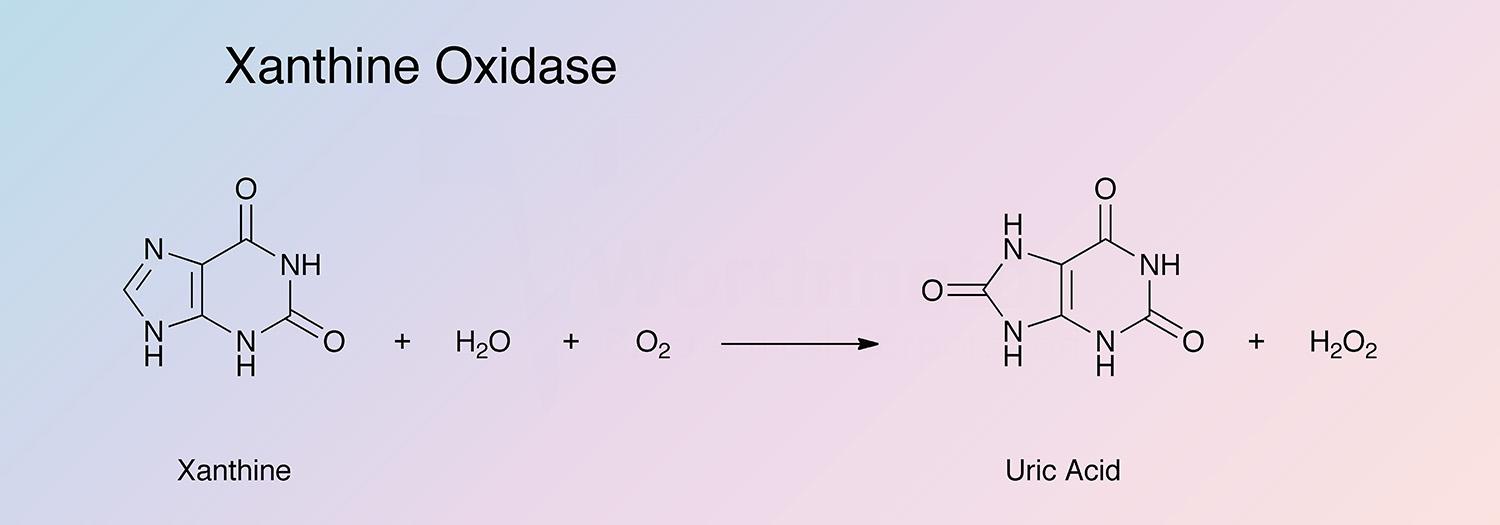
Xanthine oxidase catalyzes the oxidation of xanthine to uric acid:
Characteristics of Xanthine Oxidase from Milk:
Xanthine oxidase, being a unimolecular, multicomponent electron transport systm, has been the target of extensive study employing electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy (Bray et al. 1964; Ehrenberg and Bray 1965; Handler et al. 1964; Nakamura and Yamazaki 1969). The enzyme has been reported to have anti-tumor effect in mice (Haddow et al. 1958) and to participate in the release of iron from hepatic ferritin stores in the plasma (Mazur et al. 1958).
The enzyme has a broad specificity catalyzing the reduction of O2, cytochrome c, NO-3, Fe(CN)6-3 and various quinones and dyes by aldehydes and purines (Nakamura and Yamazaki 1969).
Each protein molecule contains 2 moles FAD, 2 gram-atoms Mo, and 8 gram-atoms Fe. The amino acid composition has been determined (Hart et al. 1970).
275,000 (Hart et al. 1970).
4.6 (Westerfeld et al. 1959).
 = 11.26 (Massey et al. 1969).
= 11.26 (Massey et al. 1969).
Metal ions, urea, purine 6-aldehyde, 2-amino-4-hydroxypteridine 6-aldehyde (Westerfeld et al. 1959).
Ammonium sulfate suspensions of the enzyme are stable for weeks when refrigerated, and for several days at room temperature.
Salicylate, cysteine, histamine, and versenate act as stabilizers.