For our international customers, please be advised that orders cannot be placed through our website by customers in countries with International Distributor representation.
RNA Polymerase - Manual
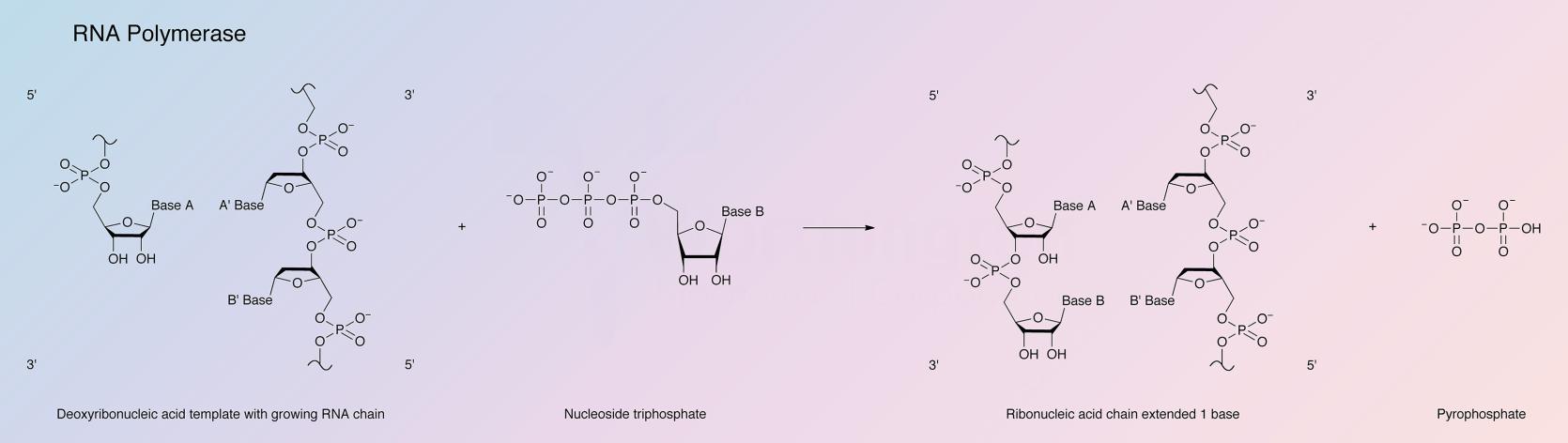
E.coli DNA-dependent RNA polymerase catalyzes the initiation (site selection), elongation and termination of polyribonucleotide chains, using ribonucleoside triphosphates as substrates and DNA as template.
Characteristics of RNA Polymerase from E. coli:
Activators and inhibitors: E. coli RNA polymerase has absolute requirements for divalent metal ions such as Mg++, Mn++, or Co++. Rifampicin, streptovaricins, streptolydigin, and sulfydryl reagents are among the inhibitors of E.coli RNA polymerase.
The enzyme has a complex subunit structure with two configurations designated RNA polymerase holoenzyme and core RNA polymerase exhibiting enzymatic activity. The holoenzyme has the subunit composition σ2'ββα,and can be resolved into two components: the core enzyme σ2'ββ and the sigma factor. The holoenzyme appears to be involved in the synthesis of most cellular RNA.
The enzyme consists of four major subunits designated β',β, α, and σ with molecular weights in that order: 160, 150, 86, 40 Kda.